The Robinhood IRA: Everything You Need To Know
- January 19, 2024
- 7 min read
-
1700 reads
Robinhood is a popular investment platform known for its user-friendly interface and commission-free trades.
With their newly launched IRAs, you get a 1% match on everything you invest with Robinhood from an outside account.
In this post, we’ll take a closer look at the Robinhood IRA, its benefits, how it works, and its advantages.
Here’s what we’ll cover in this post:
- •How Does Robinhood’s IRA Work?
- •Here’s how Robinhood’s IRAs work:
- •Robinhood Roth IRA
- •Recommended Portfolios
- •5 Advantages of Using Robinhood’s IRAs
- •1. Matching Contributions
- •2. Low Fees
- •3. Account Protection
- •4. Convenience and Accessibility
- •5. Investment Options
- •How Do Robinhood’s Matching Funds Work?
- •Who Can Invest In a Robinhood IRA?
How Does Robinhood’s IRA Work?
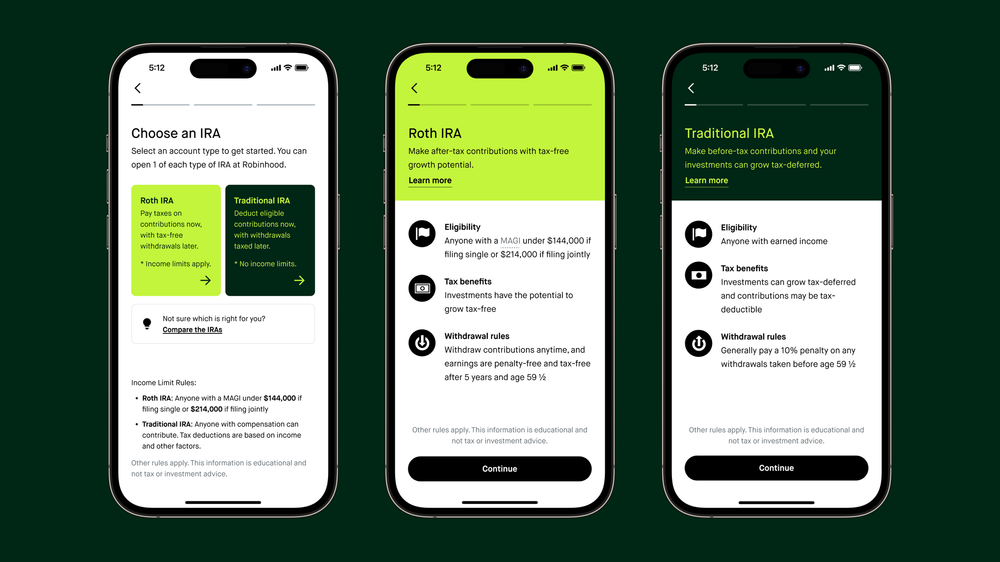
Robinhood has two IRAs: a traditional IRA and a Robinhood Roth IRA.
Similar to traditional IRAs, Robinhood’s IRAs have all the same features with one unique benefit – a matching contribution.
Here’s how Robinhood’s IRAs work:
Open an IRA
To get started with Robinhood’s IRA, you will need to open an account. This can be done easily and quickly through the Robinhood app. Simply sign up for an account and choose the option to open an IRA.Make contributions
You can make contributions to your Robinhood IRA at any time, up to the annual contribution limit set by the government.Matching your contributions
Up to a specific amount, Robinhood will match a part of your contributions. This distinctive quality distinguishes Robinhood from other investment platforms.Invest your funds
You can invest your money the same way you would with any other Robinhood account after making contributions and utilizing the matching option. As a result, you have a vast selection of stocks, ETFs, and cryptocurrencies from which to build your portfolio.It’s important to note that Robinhood charges the same reasonable costs for its IRA account as it does for its standard brokerage accounts.
This entails that you can begin saving for retirement and utilize the function of matching contributions without incurring significant costs.
👉 Get Early Access to Robinhood’s IRA
Robinhood Roth IRA
If you’re looking for a Roth IRA, Robinhood allows you to contribute your after-tax dollars to help save up for your retirement years.
With a Roth IRA from Robinhood, you can contribute up to $6,500 if your income is under $144,000 for the year (or $214,000 if you file jointly). If you are over the age of 50 you can contribute up to $7,500.
Recommended Portfolios
As a Robinhood client, you’ll have access to a robo-advisor that can help by recommending ETFs or portfolios to you.
You can invest in the recommended portfolios or choose your own ETFs and stocks, or even both.
5 Advantages of Using Robinhood’s IRAs
Robinhood’s IRAs come with several advantages that make them an excellent option for anyone looking to start saving for retirement.
Here are some of the key benefits:
1. Matching Contributions
The special feature of matching contributions offered by Robinhood’s IRAs is a wonderful incentive to get started on retirement savings.
For anyone wishing to start saving for retirement, this feature sets Robinhood apart from other investment platforms and makes it a smart choice.
2. Low Fees
Robinhood is known for its low fees, and this is also true for its IRAs. This means you can start saving for retirement and take advantage of the matching contributions feature without paying high fees.
3. Account Protection
Robinhood is a member of SIPC, which provides up to $500,000 in protection for consumers of its members who purchase securities (including $250,000 for cash claims).
4. Convenience and Accessibility
Robinhood’s IRAs can be easily opened and managed through the Robinhood app, which makes it convenient and accessible for everyone.
This means that you can start saving for retirement from the comfort of your own home, without the need for a traditional brokerage account.
5. Investment Options
Robinhood’s IRAs allow you to invest in a wide range of stocks, ETFs, and cryptocurrencies, just like its traditional brokerage accounts.
This means that you can build a diverse portfolio and take advantage of the matching contributions feature while still having control over your investment choices.
How Do Robinhood’s Matching Funds Work?

As mentioned, on every dollar invested, Robinhood matches it with 1%. This means that the extra 1% match in contributions could grow to $25k in 45 years*.
Here’s an example scenario based on the above:
- You make a contribution of $6,500 to your IRA every year. This comes to a monthly contribution of $541 or a $5.41 match.
- You earn a 1% match every year which will total $5.41 per month.
- You invest your full IRA match amount every year and earn 8% interest over the next 45 years.
- This assumes that the contribution limit is $6,500 per year.
Who Can Invest In a Robinhood IRA?
To invest you must have a Robinhood account and earn an income.
This is because the IRA only allows people who earn an income to invest in an IRA. Note that this refers to income from work, not from passive investment income.
You also need to:
- Be at least 18 years old
- Be a US citizen or lawful resident
- Have a valid SSN
- Have a US address
Anyone who earns an income can open a traditional IRA account but keep in mind that over time the tax deductions are reduced for higher incomes.
People who fall within high income brackets may not qualify to open a Roth IRA.
Robinhood IRA – FAQs
Does Robinhood have Roth IRA?
Is Robinhood safe for IRA?
What is the income limit for Robinhood IRA?
* The IRA Match is automatically added after eligible contributions from an external bank account. Keep the contributions in your IRA for at least 5 years from the date you contribute. IRA Match FAQ. Other fees may apply. See our Fee Schedule for more details.