What is the Put/Call Ratio?
A put/call Ratio reflects the proportion of put and call options that are purchased for a given market each day. The ratio is commonly used as a contrarian indicator as it reflects whether option buyers are bullish or bearish.
When traders are bearish, more put options are purchased, and this often occurs at short-term lows. When traders are bullish, more call options are purchased and this often coincides with a short-term high. Like most contrarian indicators, the P/C ratio is of the most value when it reaches extreme levels.
This ratio can be calculated for options on specific securities or indexes, or for all the options in a market. In this article, we are primarily referring to the P/C ratio for equity options traded on the Chicago Board Options Exchange (CBOE). This exchange is the largest derivative exchange in the world, so sentiment on this exchange is a good indicator for global market sentiment.
How to calculate the Put/Call Ratio?
The put/call option for a given day is simply the number of put options traded divided by the number of call options traded:
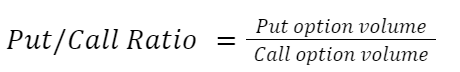
There are several variations on this ratio to consider.
Time frame
The basic calculation uses the volume of options traded on a given day. However, there are several other ways to calculate the volume:
- Weekly volume (Monday to Friday).
- Rolling 5-day volume.
- Open interest – the total number of open option contracts.
Equity options, index options or total options?
The CBOE reports trading volumes for equity options, index options and the total volume, which includes both. There are some significant differences between these markets to be aware of.
Non-professional traders who have a bullish bias primarily trade equity options. Investors also sell call options when they are bearish, which also contributes to call option volume. This means the put/call ratio is almost always lower than 1, as call volumes exceed put volumes.
Professional fund managers primarily use index options to hedge portfolios. Because put options are used to hedge downside risk, put volumes are almost always higher in this market. The P/C ratio for index options is usually higher than 1.
Total option volume includes equity options and index options. The put/call ratio for this metric oscillates above and below 1.
What is the current Put/Call Ratio?
The current put/call ratio for CBOE equity options is 0.66.
- The highest level of the last 12-months was 0.82 recorded on 21 January 2022
- The lowest level of the last 12 months was 0.35 recorded on 8 June 2021
- The current put/call ratio for CBOE index options is 1.08.
- The current total put/call ratio for CBOE equity and index options is 0.96.
What is a good Put/Call Ratio for investing?
When the put call ratio rises, it indicates that the market is becoming more bearish, and when it falls it indicates the market is becoming more bullish. Put/Call ratios are primarily used to identify short-term reversal points – so a bearish reading is seen as bullish and a bullish reading is seen as bearish.
Reversals typically occur when the ratio reaches extreme levels relative to recent highs and lows. The average P/C ratio and the range between its highs and lows can change significantly over time as market conditions change.
High P/C ratio
In 2021, short term bullish reversals occurred when the ratio for equity options was higher than 0.55.
Average P/C ratio
In 2021, the P/C ratio for equity options was mostly between 0.45 and 0.55.
Low P/C ratio
In 2021, short term bearish reversals occurred when the ratio for equity options was lower than 0.45.
How to use the Put/Call Ratio?
This ratio is typically used as a contrarian indicator, but it can also be used as a gauge of momentum and directional bias. The way you use it will also depend on your time horizon.
Short term traders can use the P/C ratio to anticipate turning points by waiting for it to reach extreme highs or lows relative to the extremes of the previous 6 to 12 months.
If your time horizon is longer than a few days, you can use one or more moving averages to reflect long-term trends, and what the average ratio is for a given period. You can identify changes in momentum when a short term moving average crosses a long term moving average.
There are lots of variations on the indicator regarding the data being used. As mentioned, the average and range can also vary substantially. This all means that there isn’t a universal way to use the indicator and investors usually develop their own approach and methods for using it.
As is often the case, it’s useful to use indicators like the put call ratio with other indicators. The P/C ratio is short term in nature, so it’s particularly helpful to use indicators with a longer term focus to give it some context. These include:
- AAII Sentiment
- VIX Index
- The Buffet Indicator
- Personal Saving Rate
- Margin Debt to Cash
- Velocity of M2 Money Stock
- Debt / GDP ratio
- Unemployment rate
- Shiller P/E ratio
- DXY index
What are the limitations of the Put/Call Ratio?
The biggest limitation of this indicator is that it is not universal. There are several variations on the way it can be calculated, and data from several markets can be used.
Another limitation is the fact that the ratio doesn’t account for whether options are being bought or sold. A trader might buy a call option when they are bullish or sell a call option when they are bearish, yet both trades would have the same result on the ratio.
These limitations mean that investors need to get to know the specific ratio they are using and what it may reflect.
Is the Put/Call Ratio a reliable indicator?
The put call ratio is a very useful indicator, particularly for identifying potential reversal points for the major indices. However, it is nuanced and does not have consistent overbought or oversold levels. The chart needs to be studied carefully to identify the overall trend and the recent trading range.
In addition to the Shiller P/E Ratio, you can use our complete list of 12- essential market indicators to make educated financial decisions.