Bitcoin Price Data
The live Bitcoin price today is $64,887.00 with a 24-hour trading volume of $52,576,630,840.
We update our BTC to USD price in real-time. The price of Bitcoin has changed 5.49% in the last 24 hours.
Currently, Bitcoin is the #1 largest cryptocurrency by market cap, with a live market cap of $1,279,128,250,616.00. It has a circulating supply of 19,686,968 BTC coins and a maximum supply of 21,000,000 coins.
See where to buy Bitcoin or use our Bitcoin Profit Calculator to calculate and track the performance of your investment.
What determines Bitcoin Price
The price of Bitcoin is determined by the joint forces of demand and supply in the crypto market. Bitcoin’s price is also influenced by news relating to Bitcoin as well as trends on social media. Learn more here.
In this article, we explore more details related to the price of Bitcoin and help you make the right decision.The Ultimate Beginner’s Guide to Bitcoin
What Is Bitcoin?

Bitcoin is digital cash transacted online on a peer-to-peer network secured by cryptography. It was launched in 2009 by a person or group of persons using the pseudonym Satoshi Nakamoto.
Bitcoin is fully decentralized, allowing you complete control over your money. This means no government or bank can freeze your account, restrict your expenditures, or confiscate your holdings.
The advent of Bitcoin marked a breakthrough in electronic money that led to the birth of a new financial system that currently runs parallel to the traditional financial system.
This new financial system came to be known as decentralized finance – an ecosystem of financial products delivered in a peer-to-peer fashion.
- Bitcoin is the first cryptocurrency in existence. It was launched as an alternative to fiat money. This means Bitcoin cannot be controlled by any bank, government, or institution. It is known as a cryptocurrency because it is secured by cryptography.
- The premier cryptocurrency was launched in 2009 by a person or group of persons using the pseudonym Satoshi Nakamoto shortly after the 2008 global economic crisis that caused millions to lose faith in governments and large institutions.
- In a whitepaper published in 2008, Satoshi Nakamoto proposed “A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System” that ran independently of a central authority.
- Bitcoin has an economic profile similar to gold: It has a limited supply and is deflationary in nature. The popular cryptocurrency is also the most valuable cryptocurrency by market cap.
- New bitcoins are created through a process called mining which involves the computation of complex math puzzles. This makes it difficult to mint new bitcoins into existence.
- The infrastructure on which Bitcoin operates – the blockchain – is a highly secure, decentralized public ledger.
- Blockchain technology has been tipped with revolutionary potential with possible applications in supply chain management, identity management, voting, and government administration.
Because it runs in a peer-to-peer format, Bitcoin is available to just about anyone, anywhere in the world. Before Bitcoin, it was not possible to send and receive money without a third-party intermediary like a bank or payment processor.
What’s more, the way traditional finance is set up means that a good chunk of the world’s population can’t participate in the system.
To solve these problems, Bitcoin runs in a peer-to-peer fashion (without a trusted third party). This means that two parties can engage in a transaction without a third-party intermediary facilitating the transaction.
Because Bitcoin cuts out the middleman (financial institutions), it is a cheaper alternative to sending and receiving money around the world.
The underlying technology that makes Bitcoin possible – the blockchain – is a distributed database powered by a peer-to-peer network secured by cryptography.
You can think of the Bitcoin blockchain as a highly secure, decentralized public ledger. A ledger is simply a record of transactions. So the Bitcoin blockchain is basically a censor-proof record of transactions.
Because the blockchain is highly secure, records on the ledger cannot be altered. Because the ledger is public, anyone can view it and track transactions happening in real time.
Because the ledger is decentralized, it cannot be hacked since there is no single point of attack.
What Determines the Price of Bitcoin?
The price of Bitcoin is determined by the joint forces of demand and supply in the crypto market. The price is also influenced by news relating to Bitcoin as well as trends on social media.
Bitcoin’s price has also been influenced by its adoption rate. The increase in investment dollars allocated to Bitcoin has caused its price to surge over the years.
The increasing adoption of Bitcoin by retail investors has also attracted the fancy of institutional investors who have poured billions of dollars into the crypto market.
In essence, the fall in future supply and the rise in demand by retail and institutional investors have kept the price of Bitcoin on an upward trajectory over the years.
Other factors that affect Bitcoin’s price include regulatory interventions as regards crypto and social media trends.
Bitcoin Price Prediction
Bitcoin has the largest market capitalization in the crypto market currently (as of March 2023). Here is the Bitcoin price prediction for 2025 and 2030 respectively:
Bitcoin has a maximum supply and only a small amount of BTC is created each day: that amount is cut in half every four years in an event called halving.
This means that if Bitcoin sustains its demand over time, it will double its value every four years. This is why the value of Bitcoin grows exponentially every four years.
Since Bitcoin has a dominant position in the crypto market, a Bitcoin rally usually translates to a crypto market rally.
Bitcoin Price History
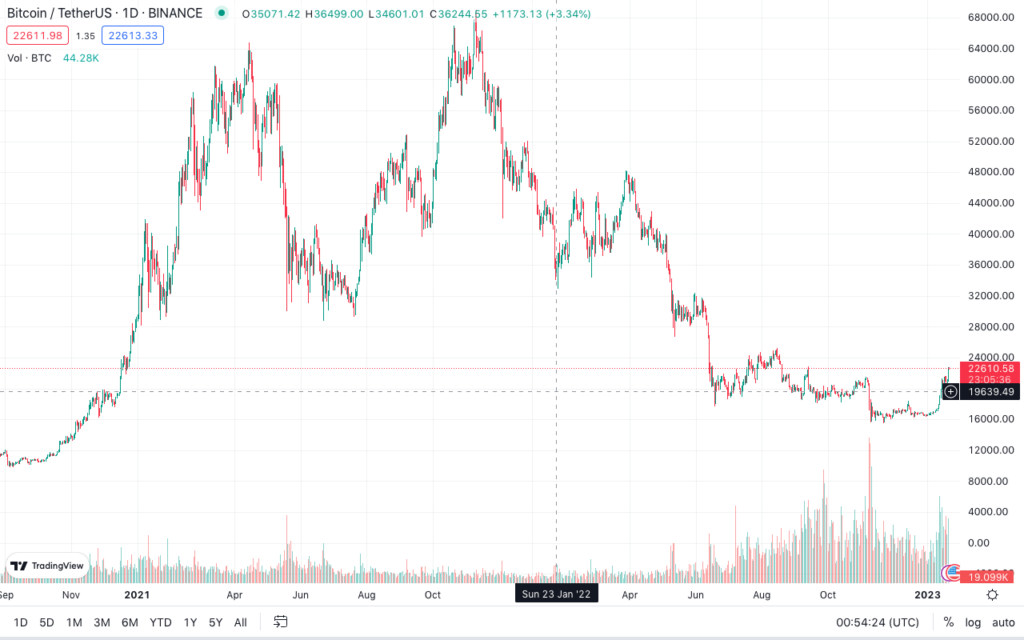
The price of Bitcoin has grown by leaps and bounds over the years moving from less than a dollar in 2010 to over $60,000 in 2021!
Between 2013 and 2014, Bitcoin grew significantly – from just $13 USD to $750 USD. But the ‘Golden Period’ for Bitcoin was between December 2017 to February 2018.
Bitcoin prices reached an all-time high of $68,789 in November 2021 but have since followed a downward trend. However, prices are expected to recover in coming years even though it’s not easy to accurately predict future prices.
It is estimated that Bitcoin prices will surpass $44,200 by the end of 2023.
Major market rallies seem to align with the halving of Bitcoin which means that a major rally might be around the corner since the next halving is scheduled for early 2024.
How Does Bitcoin Work?
There are three key parts in the Bitcoin technology stack. First is the underlying decentralized ledger – the core blockchain. Second is the protocol that runs on the blockchain – that is the software programs that facilitate transactions. Third, is the cryptocurrency – BTC.
These three layers – blockchain, protocol, and currency are the general structure of a cryptocurrency network. A coin is usually a currency and a protocol may have its native blockchain or run on a different blockchain.
The underlying decentralized ledger – the blockchain – is a public record of transactions maintained and updated by a network of nodes.
The transparent ledger is monitored by everyone and controlled by no one. The security and fidelity of the ledger are ensured by a system of cryptographic techniques.
To store cryptocurrency, you need a crypto wallet which is the equivalent of a bank account except that there’s no physical card that accompanies it.
It’s just an account number. Since creating a crypto wallet doesn’t require you to provide personal details, your identity is not attached to it like a bank account is.
What’s more, the cryptocurrency in your personal wallet is held by you. By contrast, in traditional finance, your savings are usually held in a bank or other financial institution.
Since your cryptocurrency is not held by a bank or some other financial institution, you have total control over the account. This means that your transactions cannot be blocked and your wallet cannot be shut down.
Consensus
Bitcoin uses Proof of Work (PoW) as its consensus algorithm. This means that miners compete to solve complex mathematical puzzles in order to validate transactions and create new blocks on the blockchain.
This also means that, unlike a Proof of Stake (PoS) consensus, users can’t stake Bitcoin as it uses PoW.
Mining
The maximum number of Bitcoin (BTC) that can be generated is 21 million. This limit is hard-coded into the Bitcoin protocol and is expected to be reached around the year 2140, as the rate of block rewards decreases over time.
Currently, the block reward is 6.25 BTC per block, which is halved approximately every four years in an event known as the “halving.”
Once all 21 million bitcoins have been mined, no more bitcoins can be created through mining rewards. However, transaction fees paid by users to miners will still be collected for validating transactions and securing the network.
Security
One of the primary security features of Bitcoin is its decentralized nature. The Bitcoin network is distributed across thousands of nodes, making it more resistant to attacks and censorship than centralized systems.
Additionally, the use of cryptographic algorithms to secure transactions and wallets makes it difficult for attackers to compromise the integrity of the system.
Read more about how Bitcoin is secured below.
Bitcoin vs Bitcoin Cash

Bitcoin’s highly secure, highly censor-proof ledger comes at a cost: relatively slow transactions when compared to traditional payment processors like credit cards.
For example, while VISA can process up to 24,000 transactions per second (tps), Bitcoin can only process only 7 tps.
As the Bitcoin network grew in popularity and adoption rates surged, this issue of slow transactions came to the fore of conversations amongst developers on the network prompting a proposed update that would allow for faster transactions.
However, the network couldn’t reach a consensus about how this update should happen or whether it should be implemented in the first place.
In the end, the original Bitcoin network split into two separate networks: Bitcoin and Bitcoin Cash.
In August 2017, proponents of Bitcoin Cash initiated a hard fork – a dissociation from the original blockchain – creating a new currency (BCH) that ran on its own blockchain. The coins are listed on exchanges as BTC and BCH respectively.
The BCH network implemented the originally planned update while the BTC network made a different update to the network.
Pros and Cons of Bitcoin
Here are some of the pros and cons of Bitcoin:
Pros
- A very accessible and versatile cryptocurrency
- It provides user anonymity and transparency
- It has a high return potential
- It is independent from a central authority
- Users can practise self-custody
Highly volatile
No government regulation
Transactions are irreversible
Cons
Environmental Impact
Bitcoin mining is energy-intensive, and the energy consumption associated with it has raised concerns about its impact on the environment.
The mining process requires significant computing power to solve complex mathematical problems and validate transactions on the network. This means that miners need to run powerful hardware that consumes a lot of electricity.
Bitcoin mining consumes around 0.5% of the world’s electricity, with a large portion coming from coal-fired power plants. This has led to concerns about the carbon footprint of Bitcoin mining and its potential impact on climate change.
Some cryptocurrencies are exploring alternative consensus algorithms such as PoS, which is less energy-intensive than Bitcoin’s PoW algorithm.
Ultimately, the environmental impact of Bitcoin mining will depend on the choices made by miners and the development of more sustainable technologies.
What Is Bitcoin Used For?
Although Bitcoin was originally created as an alternative to fiat money, it has found a number of uses that transcend this ideal.
Besides the role of sending and receiving money, you can also earn interest on your Bitcoin holdings by “staking” it.
In crypto terms, staking refers to the act of allocating your crypto assets to a Defi protocol or blockchain network and earning a reward for it.
Even if you decide to just hold Bitcoin, you are likely to see a good return on your investment over time.
Although Bitcoin has proven to be an extremely volatile asset, it has remained on an upward trajectory when viewed from a yearly perspective.
If Bitcoin supply diminishes and demand increases, you are likely to see a handsome return on your investment if you invest for the long term.
Who Is the Founder of Bitcoin?

Bitcoin was launched in 2009 by a person or group of persons using the pseudonym Satoshi Nakamoto as the first peer-to-peer digital currency that ran independently of a central authority.
In 2008, Satoshi Nakamoto published a white paper (“Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System”) that proposed a new monetary system that ran in a peer-to-peer fashion. This was shortly after the 2008 global economic crash that led to a loss of trust in big institutions and governments.
Hence the launch of Bitcoin in 2009 perfectly coincided with an era where people were seeking alternative solutions to the traditional financial system.
Since its launch, Bitcoin has instigated a movement that has led to a vibrant ecosystem of financial products delivered in a peer-to-peer manner.
Inspired by the work of Satoshi Nakamoto, Vitalik Buterin started working on Ethereum in 2013. Two years later, Ethereum launched, taking the crypto revolution even further: beyond currencies.
Today, Ethereum’s infrastructure supports a huge swath of the Defi ecosystem.
What Makes Bitcoin Unique?
Bitcoin’s uniqueness boils down to a number of reasons:
- It is a form of money that gives you full custody of your holdings.
- It is not governed or controlled by a central authority or government.
- It has an economic profile similar to gold. It has a maximum supply and only a small amount can be created each day. That amount is cut in half every four years in an event called halving.
- Your identity is not tied to your wallet address so it’s hard to know the “who” even if you know the “what”. In other words, it’s hard to know who owns what.
- Its pseudo-anonymous nature means that while Bitcoin transactions are transparent, you can’t tell who’s sending what to whom.
- The Bitcoin blockchain is censor-proof and highly secure.
- If a bad actor tried to undermine the system and input fraudulent records, his entry wouldn’t tally with 99% of the system. What this means is that the other computers in the network would simply ignore his record since it doesn’t align with the majority. This makes the Bitcoin network unique and extremely hard to undermine.
How Is Bitcoin Secured?
Bitcoin is secured by blockchain technology: a unique system of keeping records that spreads the responsibility of integrity across millions of participants on a computer network.
The Bitcoin ledger (a.k.a blockchain) is public, decentralized, and transparent which means it is maintained by a network of nodes spread across the world.
The ledger is monitored by everyone and controlled by no one. The security and fidelity of the ledger are ensured by a system of cryptographic techniques.
What this means is that for an entry to be added to the ledger, it has to be confirmed and validated by the majority of the network.
Think of a blockchain as a public ledger maintained by millions of “accountants” who have to come to a consensus before a transaction is added to the ledger.
They are the miners on the network who confirm and validate transactions before they are added to the ledger.
Because they do not work for a company or are part of a union, they can’t collude to undermine the network. They don’t even know each other.
Each one works to maintain the fidelity of the network since doing so comes with an incentive: rewards in Bitcoins.
This makes the Bitcoin blockchain secure, censor-proof, and pseudo-anonymous.