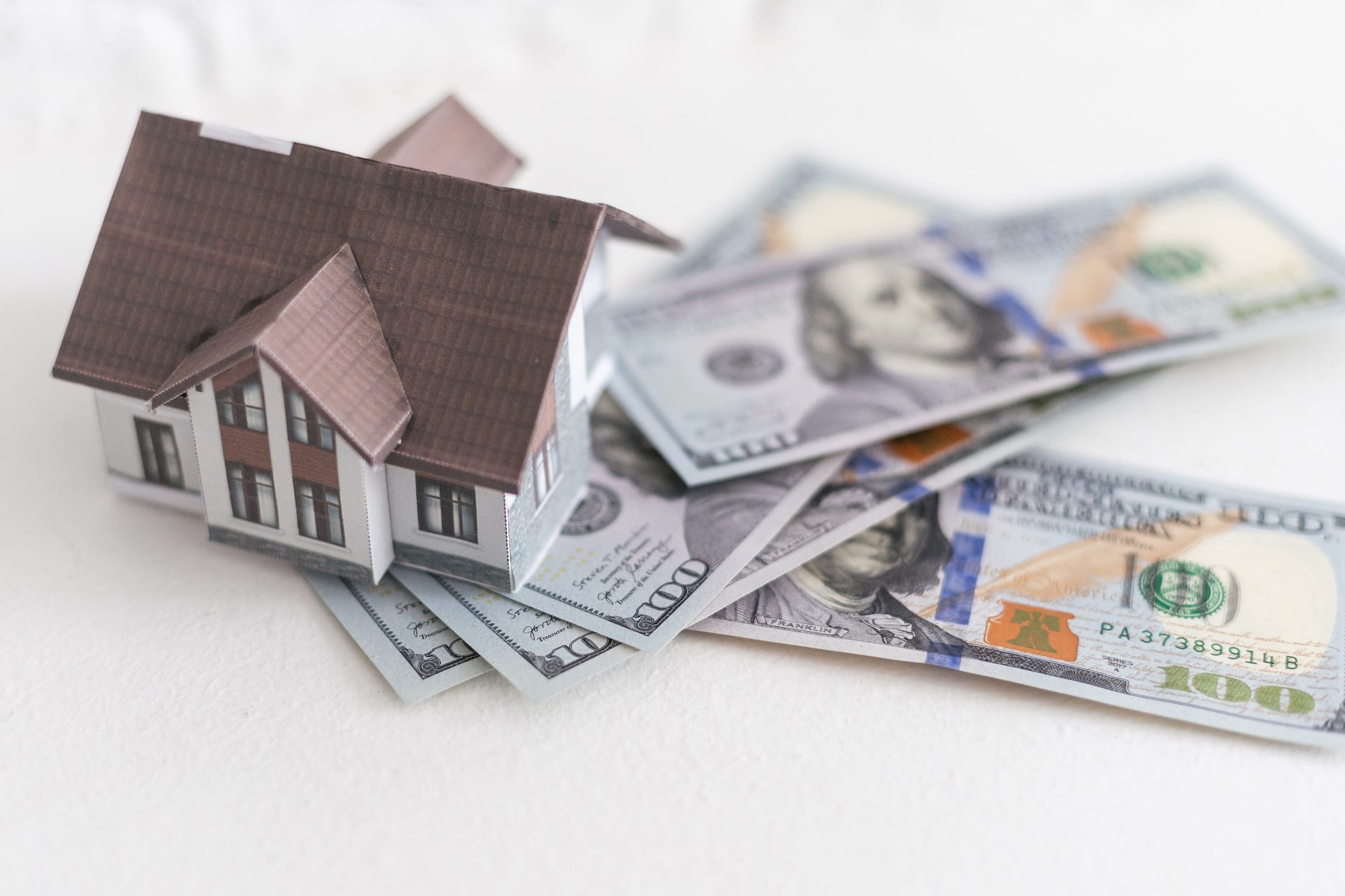
What is a Home Equity Loan?
A home equity loan, often referred to as a second mortgage, is a type of loan where you borrow money against the equity you’ve built up in your home.
Equity is the difference between your home’s current market value and the amount you still owe on your mortgage. Essentially, you’re using your house as collateral to secure the loan.
There are several reasons why someone might consider a home equity loan. These loans often provide access to large sums of cash at relatively low interest rates. This can be appealing for financing significant projects like:
- Major home renovations: Adding rooms, upgrading kitchens or bathrooms
- Debt consolidation: Paying off high-interest credit cards or other loans
- Large expenses: Covering medical bills, education costs, or unexpected emergencies.
While home equity loans can be a useful financial tool, it’s crucial to understand both the potential benefits and the risks involved. Weighing these factors carefully will help you decide if this type of loan is the right choice for your situation.
How Do Home Equity Loans Work?
Understanding the mechanics of a home equity loan is essential before you take one out. Let’s break down the key elements:
Determining Your Loan Amount
The amount you can borrow via a home equity loan hinges on two main factors:
- Home Value: Lenders will order an appraisal to establish your home’s current fair market value.
- Your Mortgage Balance: The amount you still owe on your original mortgage is subtracted from the appraised value to determine your equity.
Borrowing Limits:
Most lenders set a limit on how much equity you can tap into, typically around 80% to 85% of your home’s value, minus your outstanding mortgage.
Types of Home Equity Loans
- Lump Sum Loan: With this option, you receive the entire borrowed amount upfront. You repay the loan with fixed monthly payments over a set time period (like a traditional mortgage).
- HELOC (Home Equity Line of Credit): A HELOC functions more like a credit card. You’re granted a credit line based on your available equity. You can borrow as much or as little as you need, up to your limit, and only pay interest on what you use. HELOCs often have variable interest rates.
Interest Rates: Fixed vs. Variable
- Fixed Rate: Your interest rate stays the same over the entire loan term, providing predictable monthly payments.
- Variable Rate: Your interest rate fluctuates with prevailing market conditions. Variable rates start lower, but could rise, increasing your payments.
Repayment Terms
Home equity loans and HELOCs generally have repayment periods ranging from 5 to 30 years. The longer the term, the lower the monthly payment, but the more interest you’ll pay overall.
Benefits of Home Equity Loans
Home equity loans offer several advantages that make them an attractive option for certain financial goals:
- Lower Interest Rates: Since home equity loans use your house as collateral, they generally have lower interest rates than unsecured borrowing options like credit cards or personal loans. This translates to potential savings on interest charges over the life of the loan.
- Potential Tax Benefits: In some cases, the interest paid on a home equity loan may be tax-deductible. However, tax laws are complex and can change. It’s crucial to consult with a tax advisor to determine if you qualify for this benefit and understand any limitations.
- Versatility of Uses: Unlike some other types of loans, home equity loans don’t typically restrict how you use the funds. This flexibility offers a wide range of possibilities like home renovations, debt consolidation, and large expenses.
The benefits of a home equity loan are best realized when used responsibly. Using a home equity loan to consolidate debt only makes sense if you address the underlying spending habits that caused the debt in the first place.
Risks of Home Equity Loans
While home equity loans can be a useful financial tool, it’s essential to be fully aware of the potential risks involved before making this commitment.
Home equity loans should never be taken lightly. Thoroughly assess your financial situation, consider your risk tolerance, and weigh the potential impact on your long-term financial stability before proceeding.
- Your Home is at Risk: Since your home serves as collateral for a home equity loan, you could face foreclosure if you default on the payments. This is the most significant risk and underscores the seriousness of this type of borrowing.
- Closing Costs and Fees: Like a traditional mortgage, home equity loans often come with closing costs and fees. These can include appraisal fees, origination fees, title search fees, and more. Be sure to factor these costs into your overall financial calculations.
- Potential to Overspend: Having access to a large sum of money can be tempting. It’s crucial to have a clear plan for how you’ll use the funds and avoid the temptation to overspend on non-essential items or impulse purchases.
- Variable Interest Rate Risks: If you opt for a HELOC or a home equity loan with a variable interest rate, your monthly payment could increase if interest rates rise. This can make budgeting more difficult and lead to a financial strain.
When Does a Home Equity Loan Make Sense?
Home equity loans aren’t the right solution for everyone or every situation. However, there are specific circumstances where they could be a valuable tool:
- Necessary Home Improvements: If your home needs major renovations or repairs that you can’t afford to pay for out-of-pocket, a home equity loan can provide the funds. Focus on improvements that can boost your home’s value, potentially offsetting some of the loan’s cost.
- High-Interest Debt Consolidation: If you’re struggling with high-interest credit card balances or other loans, a home equity loan’s lower interest rate may help you pay off debt faster and save money on interest charges, especially if you have good credit.
- Major Planned Expenses: Home equity loans can be a way to finance significant expenditures like: Medical costs not covered by insurance, education expenses, large home renovation or expansion projects.
- When You Have Sufficient Equity: You’ll need a decent amount of equity built up in your home to qualify for a worthwhile home equity loan.
Less Ideal Reasons
- Everyday Expenses: Using a home equity loan to pay for recurring bills or lifestyle expenses is generally not advisable. This can put your home at risk for relatively small amounts of money.
- Non-Essential Purchases: Resist the temptation to use a home equity loan for luxury items, vacations, or other things you don’t truly need.
It’s wise to consult with a financial advisor to assess your individual circumstances. They can help you determine if a home equity loan aligns with your overall financial goals, and if other financing options might be a better fit.
Eligibility and Qualifications for Home Equity Loans
Each lender has its own specific underwriting guidelines. It’s essential to shop around and compare requirements from different lenders to find the best fit for your situation.
To qualify for a home equity loan or HELOC, you’ll need to meet certain criteria set by the lender. Here’s a breakdown of the key factors that lenders look at:
- Sufficient Equity: Most lenders allow you to borrow up to a certain percentage of your home’s value (often around 80%-85%), minus your existing mortgage balance. This means you’ll need to have built up a significant amount of equity in your home.
- Credit Score: Your credit score plays a major role in determining your eligibility and the interest rate you’ll receive. Generally, you’ll need a minimum credit score of around 620, though some lenders may have higher requirements. The higher your credit score, the better interest rates and terms you’re likely to qualify for.
- Debt-to-Income Ratio (DTI): Lenders evaluate your existing monthly debt payments compared to your gross monthly income. Most lenders prefer a DTI ratio of 43% or lower, though some may accept slightly higher DTIs.
- Income Verification: You’ll need to provide proof of stable income. Lenders want to ensure you have the means to repay the loan. Typical income documentation may include pay stubs, tax returns, and bank statements.
- Home Appraisal: Lenders will order a professional appraisal to determine your home’s current fair market value. This heavily influences how much you’re eligible to borrow.
How to Get a Home Equity Loan
If you’ve decided a home equity loan is the right path for you, here’s a step-by-step guide on how to obtain one:
Steps
Assess Your Equity
- Estimate Your Home’s Value: Use online real estate tools or talk to a realtor to get a rough idea of your home’s current market value.
- Calculate Your Equity: Subtract your outstanding mortgage balance from your home’s estimated value. This gives you a ballpark figure of your available equity.
Shop Around and Compare Lenders
- Research Lenders: Look at banks, credit unions, and online lenders offering home equity loans. Don’t just settle for the first option you find.
- Compare Rates and Terms: Obtain quotes from several lenders. Pay close attention to interest rates (fixed or variable), fees, repayment terms, and any prepayment penalties.
The Application Process
- Gather Documentation: The lender will need proof of income (pay stubs, tax returns), assets, debts, and a strong credit history.
- Home Appraisal: The lender will order an appraisal to confirm your home’s value.
Closing
- Review Loan Terms: Carefully go over the final loan agreement, including all terms and costs. Ask questions if anything is unclear.
- Sign Paperwork: If you’re satisfied with the terms, sign the necessary documents to finalize the loan.
Understanding the Fine Print of Home Equity Loans
Before signing on the dotted line for a home equity loan, it’s crucial to go beyond the advertised interest rates and delve into the details that can significantly impact the overall cost and terms of the loan.
Fees and Closing Costs: Home equity loans, like traditional mortgages, often come with various fees. These can include:
- Appraisal fees
- Origination fees
- Title search and insurance fees
- Attorney fees
- Annual fees (on some HELOCs)
Prepayment Penalties: Some lenders charge a penalty if you pay off your loan balance early. Find out if this applies and how much the penalty might be so you can factor it into your decision.
Variable Interest Rates: If you opt for a HELOC or a home equity loan with a variable interest rate, be aware that your monthly payments can fluctuate if market interest rates change. Make sure you understand how the rate is calculated and what the potential impact on your budget could be.
Balloon Payments: Some home equity loans may have a balloon payment due at the end of the loan term. This means a large lump sum payment is required to fully pay off the loan. Be sure you understand if and when a balloon payment might apply.
Foreclosure Risks: As your home is collateral, failure to make payments on your home equity loan could result in foreclosure. This underscores the seriousness of this financial commitment.
Carefully review the loan agreement and ask your lender plenty of questions before you finalize the loan. Understanding all of the terms, fees, and potential risks will help you avoid unpleasant surprises and make an informed decision about whether a home equity loan is the right choice for you.
Home Equity Loan vs. HELOC
While both home equity loans and HELOCs leverage the equity you have in your home, they function in distinct ways. Here’s a breakdown of the key differences:
| Feature | Home Equity Loan | HELOC (Home Equity Line of Credit) |
|---|---|---|
| Loan Structure | Lump sum of money | Revolving line of credit |
| Interest Rate | Typically fixed | Usually variable |
| Repayment | Fixed monthly payments over a set term | Interest-only payments during a “draw period” followed by principal and interest payments |
| Access to Funds | All funds received upfront | Borrow as needed, up to your credit limit |
| Best Uses | Large, one-time expenses (renovations, debt consolidation) | Ongoing or unpredictable expenses (medical bills, staggered home improvements) |
Additional Context
- Home equity loans are similar to a traditional second mortgage. You receive the full loan amount upfront and repay it with predictable monthly payments.
- HELOCs work more like a credit card with your home as collateral. You have a credit limit and can borrow as little or as much as you need during a set “draw period.” HELOCs often have variable interest rates, making payments less predictable.
Frequently Asked Questions
What’s the difference between a home equity loan and a HELOC?
A home equity loan provides a lump sum of money with fixed payments. A HELOC is like a credit card with your home as collateral, offering more flexible access to funds.
How much can I borrow with a home equity loan?
Lenders typically let you borrow up to 80%-85% of your home’s value, minus your existing mortgage balance.
Do I need good credit to qualify for a home equity loan?
While good credit will secure the best rates, you may still qualify with less-than-perfect credit. However, expect higher interest rates or less favorable terms.
Are there any fees associated with home equity loans?
Yes, expect closing costs like appraisal fees, origination fees, and others. These can vary between lenders.
Can I lose my home if I can’t repay a home equity loan?
Unfortunately, yes. Since your home is collateral, you could face foreclosure if you default on the loan.
Are there other options besides a home equity loan?
Yes! Depending on your goals, you might consider refinancing your existing mortgage, exploring a personal loan, or even looking at 0% interest credit cards for smaller amounts.